Traumatic injuries to the bone can happen by falls, abnormal movements or direct force to the bones. This can result in the bone breaking and is referred to as a fracture. There are many types of fractures and the nature of the injury will determine the treatment.
Closed fractures occur when there is no piecing of the skin
Open fracture
Open fractures occur when the bone pushes through the skin producing an open wound
Non displaced fracture
Non displaced fractures occur when the bone breaks, but the pieces stay in position
Displaced fracture
Displaced fracture occur when the bone breaks and the pieces move out of position
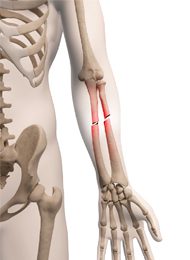
Sometimes, when the soft tissue is stronger than the bone, a small piece of bone can tear off with the muscle or tendon and create an avulsion fracture. Children have softer bones and can bend easily which makes it more difficult to break. However, if the bending or twisting is too much, the bone can snap causing a “greenstick” fracture. Other bone injuries that can occur are stress fractures and these develop as an overuse injury of repetitive small trauma. This causes small cracks in the bone that can be painful and restrict movement.
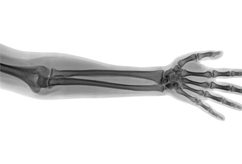
Diagnosis
The radiological findings are matched with the history and mechanics of the injury as well as a good clinical examination. Treatment is then determined accordingly.
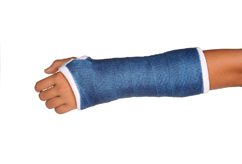
Treatment
For traumatic fractures the treatment will be determined by the orthopedic surgeon and will depend on the alignment of the bone and if there is an open wound. The treatment can include surgery to correct the bone position or casting and rest to give the bone time to grow and heal.
Recovery
Healing will usually take about 6 weeks, depending on the injury. The role of the physiotherapist after the bracing is removed is to decrease the joint stiffness that has occurred and to strengthen the weakened muscles. This is done manual techniques such as mobilization and stretches, soft tissue massage, electrotherapy and strengthening exercises.
The process of physiotherapy rehabilitation can last from 2- 12 weeks depending on the injury and weakness involved. The aim of the rehab is to achieve maximal possible range of movement, good muscle strength for daily activity, return to sport/exercise and to be as pain free as is possible.


